There are several different techniques for holding and retaining slugs that will vary based upon the material type and size. It is important to have a proper slug management plan in–place before machining begins, otherwise the machine might get damaged.
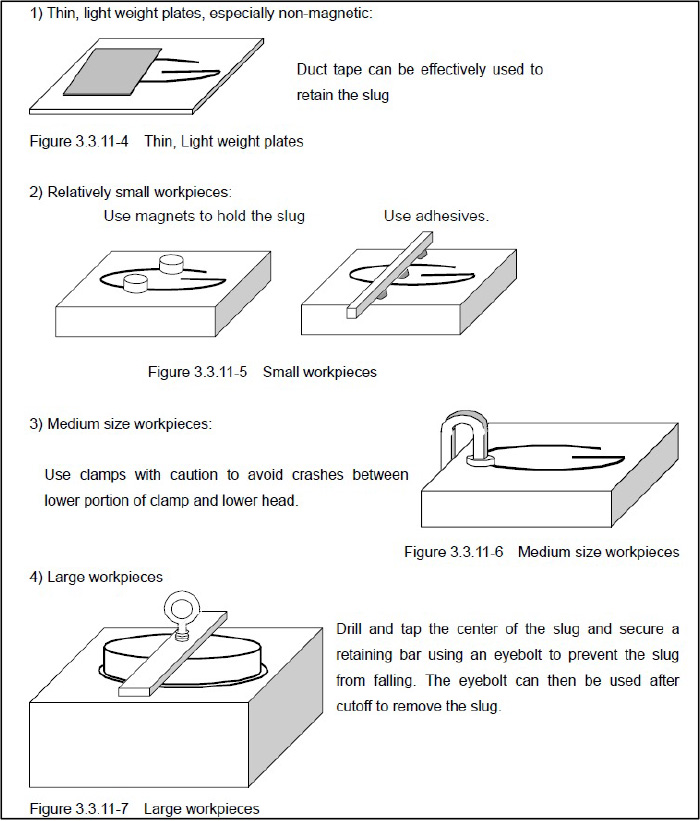
- Rare Earth Magnets: These strong magnets are a convenient and inexpensive method to control most slugs on any magnetic materials. Several different sizes and powers of magnets are available, and multiple magnets can be used to retain a slug. For Wire EDM purposes, using a lower-profile magnet will typically prevent interference and collision issues with the machine nozzles. While magnets are effective, they do have limitations. Generally, once a slug becomes larger than a 50 mm (2?) cube or greater than 5 kg (11 lbs), additional support or retaining methods should be considered.
- Adhesives: On smaller parts, glue or adhesives can be used to retain the work piece or slug, such as super glue or Bondo. This method should be reserved for smaller, lighter and more delicate part details. It is also important to have a plan in place to remove the adhesive.
- Tape: Using tape, such as duct tape, can be an effective method for controlling and retaining slugs. When machining some thin material parts, it may be necessary to apply tape mid-process, as larger, thinner materials can sag under their own weight, which will cause inaccuracies to the final part. If tape is applied mid-process, it is important to disable Automatic Wire Break recovery, as the machine could potentially crash or disturb the machine setup if the tape is placed near the program path.
- Clamps: These are simple C-Clamps or Kant-Twist clamps that are used to retain a slug from dropping. While effective, these clamps do hang below the table level, so extreme care should be taken to ensure that the machine will not crash into these clamps during operation or when moving the machine to extract the slug.
- Top Straps: These flat bars of steel are bolted to the slug before the final cutoff and dropping of the slug. This method requires pre-planning, as one or more tapped holes should be machined into the slug prior to Wire EDMing. This method is very effective on larger and heavier slugs.
- Slug Ejection via Programmable Flushing: On certain jobs where the slugs can freely fall away from the workpiece, programmable flushing can be utilized to automatically eject the slug. Depending on requirement, slugs and be pushed down and out the bottom of the part (higher pressure on upper head, lower pressure on lower head), or slugs can be pushed up and out from the top (higher pressure on lower head, lower pressure on upper head). In either case, the use of programmable flush for automatic slug ejection is typically reserved for smaller-sized slugs and dependent on the machine offering different flush pressures between the upper and lower heads.